ISO 9001:2015 Clauses 6.2 & 6.3 – Quality Objectives and Planning for Change in Your QMS
Introduction
Measuring customer satisfaction is just the beginning. This guide to ISO 9001:2015 Clauses 9.1.2 and 9.1.3 explains how to not only monitor customer perceptions but also how to use that data for powerful analysis and evaluation. Learn to transform feedback and operational data into actionable insights that drive real improvement throughout your quality management system. With Maxicert’s expertise in ISO certification and QMS implementation, organizations can establish effective monitoring practices and leverage data-driven insights to make informed, impactful business decisions.

9.1.2 Customer Satisfaction
Clause 9.1.2 of ISO 9001:2015 requires organizations to monitor and review customer perceptions to assess how well their needs and expectations are being met. This involves using methods like surveys, complaints, compliments, or feedback analysis to evaluate satisfaction and identify opportunities for improvement.
Monitoring Customer Perceptions
The organization shall monitor customers’ perceptions of the degree to which their needs and expectations have been fulfilled. The organization shall determine the methods for obtaining, monitoring, and reviewing this information.
Note: Examples of monitoring customer perceptions can include customer surveys, customer feedback on delivered products and services, meetings with customers, market-share analysis, compliments, warranty claims, and dealer reports.
How Satisfied Are Your Customers?
The standard makes it clear that you are to use customer perception as a measure of the performance of your quality management system in meeting customer requirements.
You are required to monitor information on the customers’ perception of how well you satisfied their needs and expectations—that is, your performance as a supplier.
Monitoring of customer satisfaction should be performed on an ongoing basis.
The results of your customer satisfaction monitoring should be addressed in your management review and continual improvement activities to identify and implement changes that will improve the relationship with your customers.
More Than One Type of Customer
This requirement should not be underestimated. One of the quality principles highlights its importance. You can have more than one type of customer. For example, if you are a manufacturer, you might have wholesalers, retailers, and then the general public. They all have different requirements. For your products to sell successfully, you will need to satisfy them all.
ISO 9001:2015 Clause Guide Panel
- Clause 1
- Clause 2
- Clause 3
- Clause 4 – Sub-clause 1
- Clause 4 – Sub-clause 2
- Clause 5 – Sub-clause 1
- Clause 5 – Sub-clause 2
- Clause 5 – Sub-clause 3
- Clause 6 – Sub-clause 1
- Clause 6 – Sub-clause 2
- Clause 7 – Sub-clause 1
- Clause 7 – Sub-clause 2
- Clause 7 – Sub-clause 3
- Clause 7 – Sub-clause 4
- Clause 8 – Sub-clause 1
- Clause 8 – Sub-clause 2
- Clause 8 – Sub-clause 3
- Clause 8 – Sub-clause 4
- Clause 8 – Sub-clause 5
- Clause 8 – Sub-clause 6
- Clause 8 – Sub-clause 7
- Clause 8 – Sub-clause 8
- Clause 8 – Sub-clause 9
- Clause 8 – Sub-clause 10
- Clause 8 – Sub-clause 11
- Clause 8 – Sub-clause 12
- Clause 9 – Sub-clause 1
- Clause 9 – Sub-clause 2
- Clause 9 – Sub-clause 3
- Clause 9 – Sub-clause 4
- Clause 10
Satisfaction and Dissatisfaction Are Not Opposites
Understand that satisfaction is not the opposite of dissatisfaction. If customers are dissatisfied, they could react quite badly or strongly, producing a strong negative response. Customers can also have a very strong positive response, i.e., one of delight (something beyond the normal level of satisfaction).
However, it is often the case that satisfaction produces a neutral response. Other customers who are dissatisfied may choose not to respond at all. In this case, they simply transfer their business to another supplier. Without ongoing monitoring, these neutral or less obvious responses are not easily detected by the organization.
How Many Customers Should Be Monitored?
The costs of monitoring all customers might be prohibitive; therefore, you should make a judgment based on criteria such as:
- What is the impact of any individual customer on your organization?
- How critical is your product or service to your customer’s organization?
- Are you a volume producer, or a single batch manufacturer or service provider?
- What degree of repeat business will be provided by individual customers?
This will enable you to determine how many, or which customers should be proactively monitored.
Methods of Monitoring Customer Perception
There are many ways of finding out what your customers think about how well your organization has met their requirements. For example, you may use:
- Telephone calls made periodically or after delivery of products
- Questionnaires and surveys
- Complaints, monitoring your accounts receivable, warranty claims, etc.
- Suggestions or compliments received from the customer
- Internal enquiries among your personnel who are in contact with customers
- Analysis of lost business
It is recommended that you start with simple methods such as monitoring complaints, suggestions, or compliments from your customers, or enquiries among your personnel. Surveys and questionnaires are time consuming and expensive to process. If you do use a questionnaire, then try to keep it simple, choose your questions very carefully, ensure that they are clear, and pilot test it before use.
What Customer Satisfaction Is and what is not
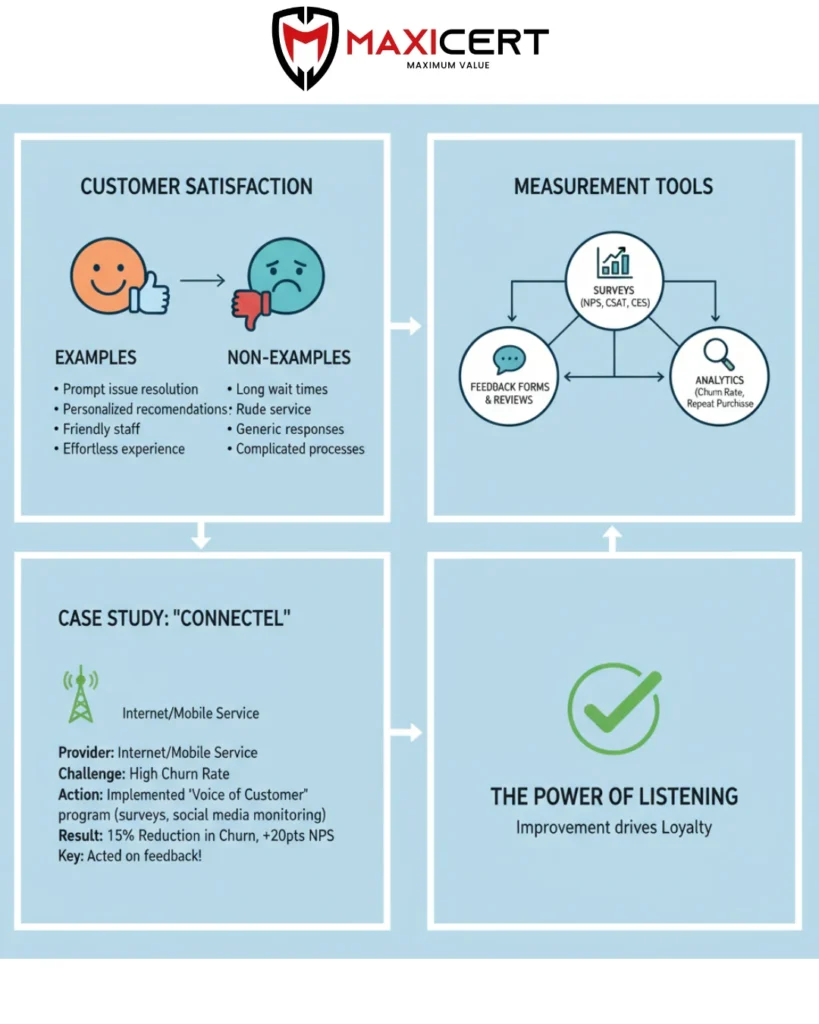
Importance of Quality Information and a Proactive Approach
The quality of the collected information depends on the ability of the organization to create and develop a proactive method to listen and analyze every input received from customers. Use the risk approach.
Industry Example: Fabrication and Construction Services for Oil & Gas Sector
A provider of fabrication and construction services in the oil & gas sector provides service to one major customer. The customer has a supplier monitoring and evaluation system in place which assesses the company’s performance at various stages of the job and gives an overall assessment at the job’s conclusion.
Quarterly reviews are done by the customer to assess the company’s performance, including a numerical score for overall company performance/customer satisfaction level. This review is documented and provided by the customer to the company.
The company uses the information obtained to identify areas where it needs to apply more effort and/or resources to increase the overall customer satisfaction score.
9.1.3 Analysis and Evaluation
Clause 9.1.3 of ISO 9001:2015 requires organizations to analyze and evaluate data from monitoring and measurement to assess product conformity, customer satisfaction, QMS performance, and improvement needs. This ensures decisions are based on facts and helps identify trends, risks, and opportunities for continual improvement.
Requirement to Analyse and Evaluate Data
The organization shall analyse and evaluate appropriate data and information arising from monitoring and measurement.
The results of analysis shall be used to evaluate:
- Conformity of products and services;
- The degree of customer satisfaction;
- The performance and effectiveness of the quality management system;
- If planning has been implemented effectively;
- The effectiveness of actions taken to address risks and opportunities;
- The performance of external providers;
- The need for improvements to the quality management system
Note: Methods to analyse data can include statistical techniques.
Do the measurements indicate any trends? This requirement highlights the importance of a factual approach to decision making, one of the seven quality management principles. Analysing data is essential for improving your quality management system, processes, and products. Simply collecting data is not enough; it must be examined, evaluated, analysed, and converted into useful proposals for decision making.
Examples of data that could be recorded and analysed include process performance deviations, training effectiveness, customer complaints, machine downtime, scrap and rework rates, missed delivery dates, supplier performance, query times, customer satisfaction levels, and cycle times.
As a result of monitoring and measurement, you will have collected significant data that can reveal trends. These trends may pinpoint problems in your quality management system or areas needing improvement. The analysis results can be used:
- As input to management review
- For corrective and preventive action decisions
- To track progress toward quality objectives
- To assess customer satisfaction
- As evidence of conformance to customer requirements
You may also identify activities that are effective but could still be improved further. Statistical techniques can be useful tools in this analysis process.
Industry Examples of Data Analysis
- Packaging Materials Supplier: Analyses data on damaged bags per batch, quality control failure rates, and customer-reported failures to demonstrate standards conformance.
- Supermarket Chain: Uses annual customer satisfaction surveys to guide management decisions, such as reducing stock-outs and adjusting package sizes.
- Technical Services Supplier: Reviews project budgets and schedules versus actual performance to verify QMS procedure conformity and process effectiveness.
- Offshore Repair Service Provider: Uses leak data to evaluate the effectiveness of planned repairs on oil platforms.
- Construction Services Provider: Tracks customer job approvals to confirm effective project planning and resource mobilization.
- Industrial Testing Laboratory: Assesses glass bottle defect types and numbers to gauge manufacturing process quality.
- Water Pump Agent: Uses delivery time data to measure on-time delivery performance.
- Oil Drilling Company: Reviews performance against quality objectives to identify improvement opportunities in fabrication, logistics, and communication processes.
Conclusion
Together, ISO 9001:2015 Clauses 9.1.2 and 9.1.3 form a powerful engine for continual improvement. Simply collecting customer feedback isn’t enough; you must also analyze and evaluate that information alongside other key performance data. By doing so, you move beyond a simple understanding of customer satisfaction to a factual, data-driven assessment of your entire quality management system’s effectiveness. This holistic approach empowers you to make smarter decisions, address root causes, and build a truly resilient organization that is constantly evolving to meet and exceed customer needs. With Maxicert’s guidance, businesses can confidently turn customer feedback and performance data into strategic opportunities for growth, improvement, and long-lasting customer trust.
Free 60–90 day implementation plan available after consultation.
Client Testimonials
What Our Clients Say About Us?
We are trusted by thousands of clients belonging from technology, manufacturing, healthcare and various sectors








Our overall experience with Maxicert was satisfied. The audit and consulting part was handled carefully, we fulfilled our client requirement of ISO 27001 hassle free.
Kevin Santiago BDM – Clarks Outsourcing, PhilippinesTimely response and knowledge of ISO standards can be seen together in the team of Maxicert, we grow because of the service providers like Maxicert.
Samuel Christopher Quality Assurance Head – OEQA, NigeriaWe did Food safety certification with Maxicert, the service was extraordinary and their consultant had good experience of the subject.
Mr. Venkatesh Production Manager - Acacia Foods and Beverages, ZambiaWe engaged a consultant of Maxicert for our business certification, we now have a well-designed and organized department procedures and we rectify our errors through internal audits regularly.
Abdullah Al Rayes Managing Director – TCS, BahrainTechnical expertise by the team of Maxicert helped us achieving our ISO 13485 certificates, we now proudly say that we have achieved our target, all thanks to the team.
Nady Boustany CEO – LMG, IraqMaxiCert's approach to meet our needs proved instrumental in facilitating a seamless transition throughout the entire ISO certification process for us. Their training sessions are so much helpful.
Ms. Latifa Al Salem Investor portfolio – Ministry of Investment, Saudi ArabiaMaxicert is a one stop solution, we got trainings, documents, audit and certification at one place, they facilitated everything.
Ms. Mariam Chaggama VP – Fasthub, TanzaniaFAQ
What does ISO 9001 Clause 9.1.2 say about customer satisfaction?
It requires organizations to regularly check how well they are meeting their customers’ needs and expectations by collecting feedback like surveys, complaints, and compliments.
Why is it important to monitor different types of customers?
Different customers have different needs, so monitoring various customer groups (like wholesalers, retailers, and end users) helps ensure everyone’s expectations are met and improves overall satisfaction.
How do organizations use customer feedback to improve?
They analyze the feedback data to identify trends or problems, then take actions like fixing issues, improving products, or changing processes to increase customer happiness.
What is Clause 9.1.3 about?
Clause 9.1.3 focuses on analyzing and evaluating all performance data, including customer satisfaction results, to see how well the quality management system is working and where improvements are needed.





Their presence in Oman made us even better to accomplish our goal of achieving ISO certificates on time, we will definitely recommend their services.
Mr. Sailesh Mohanakrishnan Division Manager – Khimji Ramdas, Oman